We acknowledge valuable contributions made by Gina Brown-Guedira during the preparation of this page.
Leaf rust resistance gene Lr46 is a slow rusting gene. These genes do not provide the host plant with complete immunity against a set of leaf rust (Puccinia triticina) races; instead they can delay the infection process or reduce the development of symptoms caused by a wider range of leaf rust races on adult plants. For more details on slow rusting genes you can visit the Lr34 page.
Lr46 was first described in 1998 by Singh et al. (1) in cultivar Pavon 76, and located on chromosome 1B. Martinez et al (2) showed that the latency period of infected adult plants was significantly lower in plants carrying Lr46 compared to the controls without the gene. Lr46 was also responsible for an increase in the fraction of early aborted fungal colonies. The type of resistance conferred by Lr46 is similar to that of Lr34, although with a smaller effect.
In 2003, William et al. (3) used AFLP markers to map Lr46 on the distal end of 1BL. The authors also found that Lr46 was tightly linked or pleiotropic to a stripe rust resistance gene designated Yr29. The tight linkage of a slow rusting gene to a stripe rust resistance gene was also found for the pair Lr34/Yr18. Suenaga et al. (4) determined that the microsatellite locus Xwmc44 is located 5.6-cM proximal to the putative QTL for Lr46.
Markers for Lr46
Lr46 was mapped distal to Xwmc44, approximately 5-15 cM, and proximal to Xgwm259, approximately 20 cM (Gina-Brown Guedira personal communication). Microsatellite locus Xbarc80 maps 10-11 cM distal to Xgwm259 and can be used as an alternative distal marker.
Marker Xwmc44
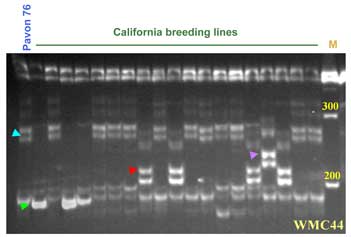
Microsatellite locus Xwmc44 maps 5-15 cM proximal to Lr46.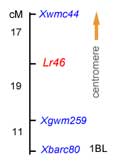
Primers sequences:
WMC44-forward 5'- GGT CTT CTG GGC TTT GAT CCT G -3'
WMC44-reverse 5'- GTT GCT AGG GAC CCG TAG TGG -3'
PCR conditions:
At the recommended annealing temperature, 61°C, polymorphic products are observed with either agarose or polyacrylamide. The expected product for Chinese Spring is a band of 242 bases.
- Denaturing step: 94°C, 3 min
- Amplification step (45 cycles):
- 94°C, 30 s
- 61°C, 30 s
- 72°C, 90 s
- Extension step: 72°C, 10 min
Expected products:
Marker Xgwm259
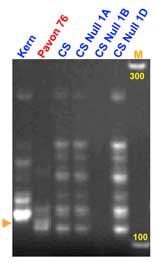
Microsatellite locus Xgwm259 maps approximately 20 cM distal to Lr46 and can be used as a flanking marker together with Xwmc44.
Primer sequences:
WMS259-forward 5'- AGG GAA AAG ACA TCT TTT TTT TC -3'
WMS259-reverse 5'- CGA CCG ACT TCG GGT TC -3'
PCR conditions:
- Denaturing step: 94°C, 3 min
- Amplification step (45 cycles):
- 94°C, 30 s
- 56°C, 30 s
- 72°C, 90 s
- Extension step: 72°C, 10 min
Expected products:
Marker Xbarc80
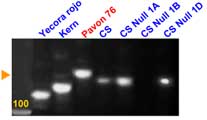
Microsatellite locus Xbarc80 maps 10-11 cM distal to Xgwm259, and can be used as an alternative distal marker.
Primers sequences:
BARC80-forward 5'- GCG AAT TAG CAT CTG CAT CTG TTT GAG -3'
BARC80-reverse 5'- CGG TCA ACC AAC TAC TGC ACA AC -3'
PCR conditions:
- Denaturing step: 94°C, 3 min
- Amplification step (45 cycles):
- 94°C, 30 s
- 50°C, 30 s
- 72°C, 60 s
- Extension step: 72°C, 10 min
Expected products:
Available germplasm
Lr46 was first discovered in cultivar 'Pavon 76' (PI 519847), and transferred to susceptible cultivars like 'Jupateco 73' and 'Avocet' (1). Also, substitution lines of line Lalbahadur with the chromosome 1B of 'Pavon 76' were developed (2). Another original source for Lr46 was cultivar Parula (PI 520340).
References
1. Lr46: A Gene Conferring Slow-Rusting Resistance to Leaf Rust in Wheat. Singh RP, Mujeeb-Kazi A, Huerta-Espino J. In: Phytopathology, 1998, 88(9):890-894.
2. Characterization of Lr46, a gene conferring partial resistance to wheat leaf rust. Martínez F, Niks RE, Singh RP, Rubiales D. In: Hereditas, 2001, 135:111-114.
3. Molecular Marker Mapping of Leaf Rust Resistance Gene Lr46 and Its Association with Stripe Rust Resistance Gene Yr29 in Wheat. William M, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Ortiz Islas S, Hoisington D. In: Phytopathology, 2003, 93(2):153-159.
4. Microsatellite Markers for Genes Lr34/Yr18 and Other Quantitative Trait Loci for Leaf Rust and Stripe Rust Resistance in Bread Wheat. Suenaga K, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, William HM. In: Phytopathology, 2003, 93(7):881-890.
