Stem rust resistance gene Sr21 confers resistance to several races of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici, including those in the Ug99 group. But contrasting studies reported both susceptible and partial resistant reactions. Sr21 was first identified in diploid wheat Triticum monococcum (1) and later transferred to hexaploid wheat (2), where it was mapped on chromosome arm 2AL, 2.4 cM distal from the centromere. However, this distance might not be precise because chromosomes of T. monococcum and T. aestivum recombine poorly in the presence of the Ph1b gene.
To clarify this point, improve its chromosomal location and determine the value of Sr21 in breeding, Chen et al. (3) developed two large mapping populations of diploid wheat. In addition, since the variations in Sr21 resistance seemed to be affected by environmental variables, they tested if temperature and photoperiod modulated the resistance provided by this gene.
One of the mapping populations was derived from a cross between T. monococcum ssp. monococcum PI 272557 (susceptible) and the spring line DV92, which is supposed to carry Sr21 and Sr35. The other mapping population resulted from a cross between PI 272557 and G3116, a wild winter line of T. monococcum subsp. aegilopoides that was postulated to carry Sr21.
The effect of temperature on Sr21 resistance was studied at 16, 20 and 24 °C and the photoperiod was evaluated at 10, 15 and 20 hours. The results shown that the recombinant lines carrying Sr21 were susceptible at 16 °C, but resistant at 20 and 24 °C to the Ug99 races tested. In comparison, the effect of photoperiod was smaller and only slight differences in infection type were observed under different photoperiods.
More recently, Chen et. al (4) carried out a sequencing analysis of the genomic region corresponding to Sr21 and found four nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat protein (NLR) genes linked to the Sr21 phenotype. Through further genetic, mutagenic and complementation testing, they determined that the CNL1 gene was the best candidate for Sr21, and developed perfect markers for it.
Sr21 can be deployed in breeding programs to provide Ug99 resistance. As usual, it has to be combined with other sources of resistance. This recommendation is especially important in this case due to the environmental effects that affect its effectiveness.
Markers for Sr21
The effective allele of Sr21 introgressed into hexaploid wheat from Triticum monococcum can be monitored by the perfect PCR-CAP marker Sr21TRYF5R5, followed by digestion of the amplification product with NsiI (4).
Primer sequences:
Sr21TRYF5R5-F 5'- CCT AGA GAA ACG GAA GGG ACC A -3'
Sr21TRYF5R5-R 5'- TGT GAG CTG TTT GCA GAA GTG TG -3'
Assay conditions
- Annealing temperature: 56°C
- Digestion of the amplification product with restriction enzyme NsiI
Expected products:
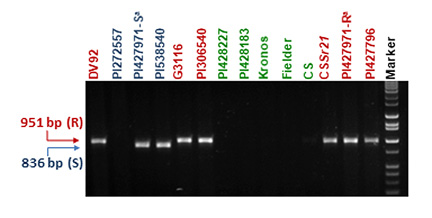
Typical results are shown in Fig. 1. Susceptible T. urartu, tetraploid and hexaploid wheat lines do not amplify. A 951-bp fragment is produced when the T. monococcum haplotypes are present. Treatment with enzyme NsiI generates two bands of 836 and 115 bp for T. monococcum accessions carrying the Sr21 susceptible haplotypes, and a single 951-bp band for the accessions carrying the resistant haplotypes.
Other markers for Sr21
Two very close CAP markers are FD527726 (0.15 cM, distal) and EX594406 (0.05 cM, proximal). Another useful marker is SSR gwm312, 0.2 cM on the proximal side.
Primer sequences:
gwm312
WMS312-F 5´- ATC GCA TGA TGC ACG TAG AG -3´
WMS312-R 5´- ACA TGC ATG CCT ACC TAA TGG -3´
Annealing temperature 60 °C
FD527726
FD527726-F 5´- CGG CAT CAA TAG GAG AAG A -3´
FD527726-R 3´- TAG GAT ACG TGA CCC AGG A -3´
Annealing temperature 53 °C
EX594406
EX594406-F 5’- TCA ACA ACT TCA ACA AGG C -3´
EX594406-R 5’- AAC AAG AGA ACG AGC ATC G -3´
Annealing temperature 52 °C
PCR conditions:
- Denaturing step: 94°C, 5 min
- Amplification step (40 cycles):
- 94°C, 30 sec
- 50-60 °C (depending on the primer pair), 30 sec
- 72°C, 60 sec
- Extension step: 72°C, 7 min
FD527726 and EX59446 are CAP markers, requiring an extra step of treatment with a restriction enzymes BsrDI and XmnI, respectively.
PCR reaction mix
- 1 unit Taq DNA polymerase
- 2 µL 10X buffer
- 1.5 mM MgCl2
- 0.2 mM dNTP
- 0.5 µL of each primer (10 µM)
- 50 - 100 ng template DNA.
Total: 20 µl
Expected products:
PCR products were separated in 6 % non-denaturing acrylamide gels or 1 % agarose gels and stained directly with ethidium bromide. The sizes of the bands associated or not to Sr21 for each marker are:
gwm312
Sr21- 180
Sr21+ 182
FD527726
Sr21- 806
Sr21+ 754
EX594406
Sr21- 420
Sr21+ 566
References
1. Chromosome location of genes conditioning stem rust resistance transferred from diploid to hexaploid wheat. The T. In:Nature New Biology, 1973, 241:256.
2. Cytogenetical studies in wheat. IX. Monosomic analyses, telocentric mapping and linkage relationships of genes Sr21, Pm4 and Mle. McIntosh R, Bennett FG. In: Australian Journal of Biological Sciences, 1979, 32:115-126.
3. Fine mapping and characterization of Sr21, a temperature‑sensitive diploid wheat resistance gene effective against the Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici Ug99 race group. Knott DR. In: Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2015, 128:645-656.
DOI: 10.1007/s00122-015-2460-x
4. Identification and characterization of wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr21 effective against Ug99 race group at high temperature. Chen S, Zhang W, Bolus S, Rouse MN, Dubcovsky J. In: PLoS Genetics. In process
